Quantitative Vs. Qualitative Data Analysis in Dissertations: When to Use Each Method
Whether working on a dissertation in the social sciences, business, or humanities, understanding the differences between quantitative and qualitative data analysis is essential for generating meaningful insights. However, due to the complexity of both methodologies and dissertation structuring, researchers may need help with data analysis in qualitative research or quantitative studies. That is why our professionals are here to ease your workload while helping you meet your academic goals with precision and professionalism by offering expert dissertation data analysis services. Seeking help from a statistician or qualitative analysis expert ensures methodological rigor and minimizes the risk of errors that compromise the credibility of dissertations. This article contains a comprehensive overview of quantitative and qualitative data analysis methods, including their definitions, key differences, pros and cons. The article also contains a discussion on the context best suited for each method.
What Is Quantitative Data Analysis?
Quantitative data analysis is the use of numerical data to discover patterns, relationships, and statistical significance. The quantitative data analysis approach is used when researchers intend to test hypotheses and measure variables or predictions. Data gathered during quantitative research is organized and processed with the help of mathematical and statistical tools.
The principles of quantitative analysis include objectivity and the quantification of data to describe or predict phenomena. The quantitative analysis employs statistical software such as the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS), R Studio, Stata, Microsoft Excel, Python, Minitab, Tableau, and SAS. Standard methods used in analyzing quantitative data are descriptive statistics (mean, median, mode), inferential statistics (t-tests, ANOVA, regression analysis), and predictive modeling. Such techniques enable researchers to test hypotheses and make generalizable conclusions based on massive data. For those working on dissertations that involve experiments, surveys, or numerical secondary data, getting help with data analysis in quantitative research is essential. Our experts code clients’ data appropriately, conduct the right tests, and interpret the results accurately. Support from experts helps to reinforce the legitimacy of study results and gives researchers more confidence in their representation.
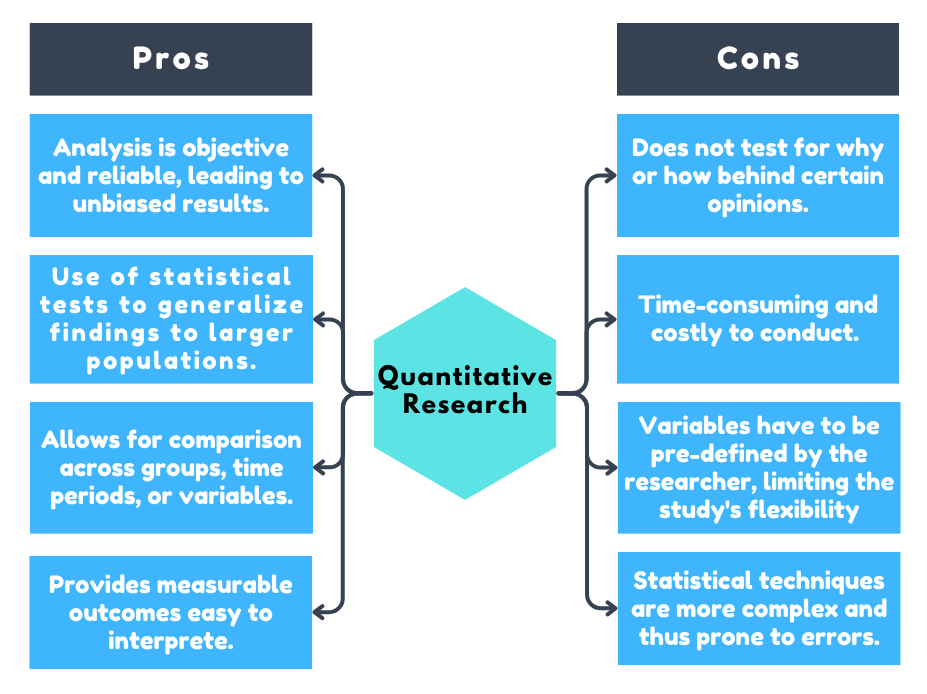
Pros and Cons of Quantitative Data Analysis
Context Best Suited for Quantitative Research Dissertation
Quantitative data analysis is best suited when the study is designed to test a specific hypothesis, involves measuring variables, and analyzing numerical data. Quantitative data analysis is also suitable when the researcher’s goal is to predict outcomes, compare groups, apply statistical inference to draw broader conclusions or identify relationships. Quantitative analysis can be used in studies evaluating the effectiveness of a new instructional approach on learners’ performance, examining the survey data to identify consumers’ preferences, and investigating the connection between the level of income and health outcomes. In situations where selecting the right tests and interpreting results accurately is critical, our data analysis specialists provide the expertise needed to avoid common mistakes and ensure reliable outcomes. With our support, you can move forward with confidence and clarity in your research.
What Is Qualitative Data Analysis?
Qualitative data analysis refers to the process of interpreting non-numerical data to identify themes, meanings, and patterns. Qualitative data analysis involves interpreting meaning, experience, or social situation. Qualitative analysis does not measure or predict but instead attempts to understand complex phenomena through observation. Thematic, grounded theory, content, and narrative analysis are the key qualitative data analysis techniques. Software packages such as NVivo, ATLAS.ti, or MAXQDA assist researchers in organizing and coding qualitative data. These software programs handle significant amounts of multidimensional, unstructured data, facilitating the discovery of trends and patterns and generating meaningful insights.
A qualitative study is interpretative and subjective, making the researcher a key tool in the analysis process. Researchers often seek help with data analysis in qualitative research to navigate challenges such as theme development, maintaining rigor, and minimizing bias. Consulting an expert in qualitative analysis gives critical feedback, builds credibility, and makes findings richly supported by data.
Pros and Cons of Qualitative Data Analysis

Context Best Suited for Qualitative Research Dissertation
There are more instances when qualitative research can be used. Some instances include when the researcher seeks to understand concepts or experiences and focuses more on depth than breadth. Qualitative analysis can be used to examine the experience of burnout in caregivers, the perception of online learning among students, and the representation of mentalhealth problems in the media.
When a researcher’s study relies heavily on interpretation and meaning, seeking help from a statistician or qualitative analysis expert ensures accuracy and depth. Our team assists clients through theory development, theme generation, and coding, helping them produce results that are methodologically sound and academically defensible. Contact us today to get expert support tailored to your dissertation research needs.
Key Distinctions Between Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis
The decision to use either quantitative or qualitative data analysis is primarily based on the research question, type of data, and outcomes. Each analysis method answers varying types of research questions. Therefore, comprehending the differences between quantitative and qualitative analysis is essential. The following are the key differences:
1. Data Type
Quantitative
Quantitative numeric data enables the researcher to measure variables and subject them to statistical analysis. These values are easy to measure and can be compared between groups or timeframes. Some examples are test scores, income brackets, blood pressure readings, or survey frequencies.
Qualitative
Qualitative data is a non-numeric type of data that mostly comprises words, pictures, or observations. Scholars interpret this descriptive and rich information to reveal deeper themes and meanings. The sources of qualitative data include interview transcripts, journal entries, video footage, and photographs.
2. Research Focus
Quantitative
The aim of quantitative research is to verify a theory or hypothesis by applying measurable variables. Researchers use quantitative studies to explore the relationships, trends, or impacts that can be measured. For example, scholars could examine the relationship between socioeconomic status and academic achievement. Comprehending quantitative research is crucial to ensure that research questions align with the proper analytical approach.
Qualitative
Qualitative research emphasizes the interpretation of phenomena in the light of the participants. Using qualitative research, scholars attempt to discover how individuals create meaning out of their own lived realities and the significance of those experiences within a particular situation or setting. Qualitative research methods are well-suited for investigating cultural practices, emotions, or social processes.
3. Data Collection Methods
Quantitative
Structured instruments are used to gather quantitative data and generate numerical outputs. These instruments are designed to minimize bias and ensure consistency across samples. Examples include standardized questionnaires, lab experiments, and government census data.
Qualitative
Qualitative data collection is flexible and adaptive to the research setting. Qualitative data collection often involves direct interaction with participants in natural environments. Methods include semi-structured interviews, ethnographic observation, and reflective journals.
4. Analysis Approach
Quantitative
Quantitative data analysis is objective and relies on established statistical procedures. Researchers use software programs such as SPSS, R, Excel, Minitab, Tableau, SAS, and Python to calculate significance, correlation, and other statistical measures. This method is suited for confirming hypotheses and measuring effect sizes.
Qualitative
Qualitative analysis is an interpretive and recursive process involving repeated review of data to identify emerging themes. Researchers use coding techniques to group and label similar ideas. Tools such as NVivo, ATLAS.ti, or MAXQDA are utilized to analyze qualitative data.
5. Outcomes
Quantitative
Quantitative findings can be generalized to broader populations if the sample is representative. The generalizability to broader populations makes quantitative results suitable for policy-making and large-scale decision-making. Researchers use the technique when predicting, measuring, and comparing outcomes utilizing numerical data.
Qualitative
Qualitative outcomes provide a deep understanding of specific cases, populations, or settings. Instead of generalizing, the emphasis is on insight, nuance, and meaning. Qualitative findings often contribute to theory development or contextual understanding rather than prediction.

Why Choose Our Help with Data Analysis in Quantitative Dissertation?
When analyzing quantitative data, precision and accuracy matter. We are a team of professionals and qualified individuals who offer custom assistance to researchers in dealing with complex statistical work. Our experts assist clients at every step, from designing surveys to selecting the appropriate statistical tests, interpreting results, and writing reports. Our professionals can help choose the relevant statistical tests and conduct complex analyses using programs such as SPSS, R, Tableau, Excel, Python, Minitab, and SAS. They also assist in accurately interpreting results and checking for errors or outliers that may influence validity.
Our affordable rates and around-the-clock customer service team ensure that researchers receive assistance anytime, whether they are up against a deadline or making final revisions before submission. Our experts are always available to assist researchers, regardless of their field of study or academic level, in conducting data analysis successfully. By hiring us, our clients get peace of mind and assurance that the quantitative analysis of the dissertation will be of high quality.
What makes Our Help with Data Analysis in Qualitative Dissertation Outstanding
Qualitative analysis requires in-depth interpretative skills, meticulous attention to detail, and a profound understanding of human behavior and context. Our experts are trained in thematic analysis, grounded theory, content analysis, and other qualitative techniques to ensure that clients’ dissertations meet all academic and institutional standards. Also, our professionals have experience in using NVivo, MAXQDA, and ATLAS.ti software to analyze and manage qualitative data.
We provide custom services that address clients’ study goals, ensuring their themes are well-developed and supported by data. We also assist with validating study findings through member checking, triangulation, or peer debriefing. Whether working with interviews, focus group transcripts, or open-ended surveys, we maintain the highest quality in helping with crafting clear, coherent, and academically sound analysis sections. Our services are affordable, allowing clients to receive premium assistance without straining their budgets.
Summary
Both quantitative and qualitative data analysis play critical roles in dissertation research. The choice of method depends on the study question, the type of data, and the objectives. Quantitative analysis is best when one intends to measure and generalize a population from a sample; qualitative analysis is ideal for exploring experiences and meanings. In some cases, using both approaches offers the most comprehensive view, known as mixed methods. Regardless of the research method, obtaining help with data analysis in both quantitative and qualitative research ensures that one’s study results are valid, credible, and defensible. For those in need of data analysis services, you contact us for help with data analysis in qualitative research today or join our live chat to speak with our friendly customer support team. We are available 24/7 to ensure that we respond to your inquiries promptly and deliver tasks on time, meeting our clients’ due dates without compromising on quality.